seaborn.diverging_palette
seaborn.diverging_palette(h_neg, h_pos, s=75, l=50, sep=10, n=6, center='light', as_cmap=False)
在两个 HUSL 颜色直接建立一个发散调色板。
如果您在使用 IPython notebook,您还可以通过 choose_diverging_palette() 函数交互式选择调色板。
参数:h_neg, h_pos:float in [0, 359]
图的正负范围的锚定色调
s:[0, 100] 范围内的浮点数,可选
图的两个范围的锚定饱和度
l:[0, 100] 范围内的浮点数,可选
图的两个范围的锚定亮度
n:int,可选
调色板中的颜色数(如果为 not,返回一个 colormap)
center:{“light”, “dark”}, 可选
调色板中心为亮或暗
as_cmap:bool, 可选
如果为 true,返回一个 matplotlib colormap 而不是一个颜色列表。
返回值:palette or cmap:seaborn color palette or matplotlib colormap
类似列表的颜色对象的 RGB 元组,或者可以将连续值映射到颜色的 colormap 对象,具体取决于
as_cmap参数的值。
另外
创建具有暗值的连续调色板。创建具有亮值的连续调色板。
例子
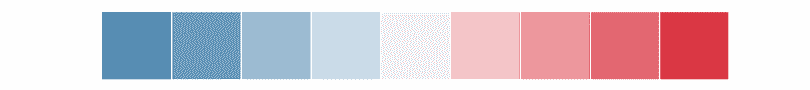
生成一个蓝-白-红调色板:
>>> import seaborn as sns; sns.set()
>>> sns.palplot(sns.diverging_palette(240, 10, n=9))
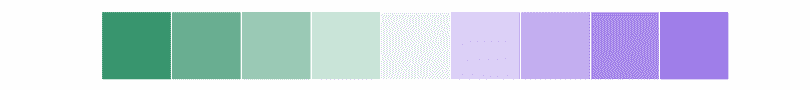
生成一个更亮的绿-白-紫调色板:
>>> sns.palplot(sns.diverging_palette(150, 275, s=80, l=55, n=9))
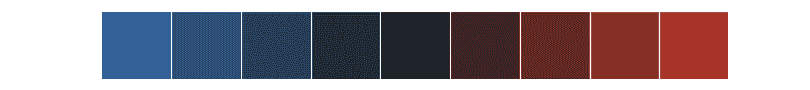
生成一个蓝-黑-红调色板:
>>> sns.palplot(sns.diverging_palette(250, 15, s=75, l=40,
... n=9, center="dark"))
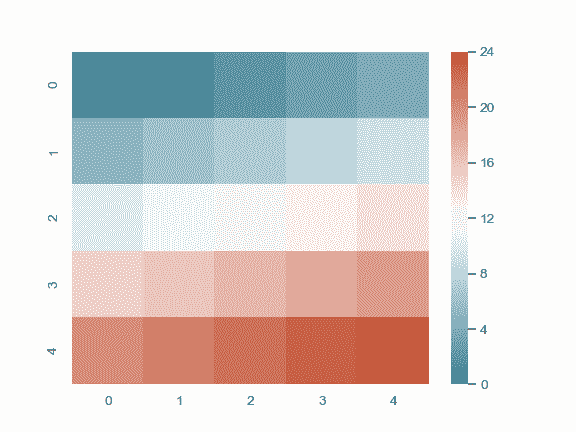
生成一个 colormap 对象:
>>> from numpy import arange
>>> x = arange(25).reshape(5, 5)
>>> cmap = sns.diverging_palette(220, 20, sep=20, as_cmap=True)
>>> ax = sns.heatmap(x, cmap=cmap)